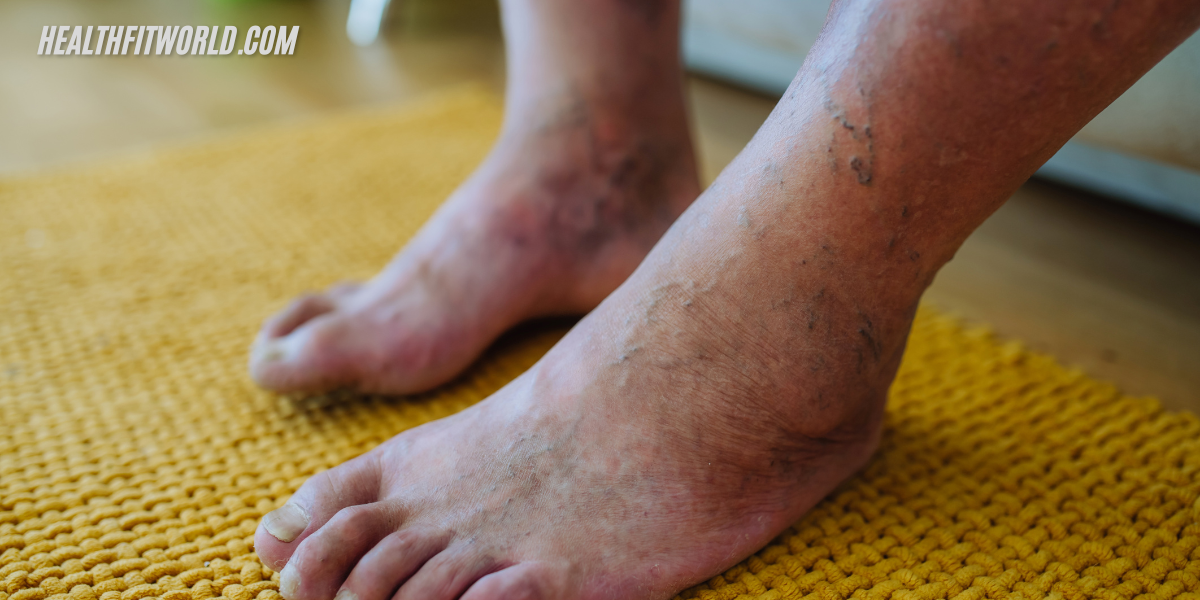
Discoloured feet can cause concern, especially when the colour change becomes persistent. One of the most common signs of an issue in the body’s circulation system is when the toes or soles take on a different hue, such as purple or blue. This can happen for various reasons, from a simple bruise to more serious conditions like Raynaud’s disease or frostbite. When blood flow is restricted or poor circulation is present, the feet are often the first to show symptoms. The blood vessels may harden, narrow, or close off, making it difficult for oxygen-rich blood to reach the feet. As a result, areas like the ankles, toes, and heels may show signs of discolouration.
Reduced circulation can cause the feet to become numb, cold, or even black. Poor circulation can also lead to discomfort or pain, especially when standing for long periods or wearing ill-fitting shoes. Understanding the reasons behind these changes is essential to seeking the right treatments. Massaging the feet, ensuring adequate oxygen flow, and visiting a doctor or podiatrist can help diagnose the problem. When blood flow is restored, most discolouration issues can heal, and blood can travel properly through the arteries and veins, improving overall health.
Foot Injuries and Discoloration
Causes of Discoloration:
Foot injuries, such as sprains, bruising, or fractures, can result in visible discolouration. The affected area may show purple, yellow, or green hues during healing.
Swelling and Immediate Care:
When an injury occurs, swelling is a typical response. Proper care is crucial to prevent further complications.
RICE Therapy for Treatment:
Using RICE therapy (Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation) can help manage swelling and pain:
- Rest: Avoid putting pressure on the injured foot.
- Ice: Applying an ice pack or frozen peas can numb the area and reduce inflammation.
- Compression: Wrapping the foot in a bandage helps support the area and improve circulation.
- Elevation: Keeping the foot elevated reduces swelling and aids healing.
Severe Injuries Requiring Medical Attention:
For more severe injuries such as fractures or frostbite, seeking medical attention is necessary to ensure proper treatment.
Pain Management
- NSAID medications can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation during recovery.
When to Seek Further Medical Advice:
- If the injury is not improving, a doctor may recommend imaging, such as an X-ray, to check for bone damage.
- Immediate medical consultation is advised if the foot turns black or the discolouration worsens.
Monitoring and Recovery:
Temporary discomfort and bruising usually indicate a minor injury. However, monitoring any changes and seeking medical help if symptoms persist or worsen is essential.

Circulatory and Vascular Conditions That Cause Foot and Leg Discoloration
1. Raynaud’s Disease and Color Changes
What is Raynaud’s Disease?
Raynaud’s disease, also known as Raynaud’s phenomenon, can cause noticeable colour changes in the feet and hands, particularly in response to cold weather or stress.
Symptoms and Color Changes:
During an episode, blood vessels constrict, restricting blood flow and leading to:
- Colour shifts: Affected areas may turn blue, purple, red, or white.
- Sensations: Individuals may experience numbness, pins and needles, or a burning sensation.
- Duration: Episodes can last anywhere from a few minutes to several hours.
Primary vs. Secondary Raynaud’s
- Primary Raynaud’s: Occurs on its own without any underlying condition.
- Secondary Raynaud’s May indicate more serious conditions such as:
- Lupus
- Scleroderma
- Sjogren’s syndrome
Who is Affected?
- Women are more commonly affected.
- Symptoms often begin in the teens or 20s.
Managing Raynaud’s Disease:
- Keep hands and feet warm to prevent attacks.
- Minimize anxiety and stress, as they can trigger episodes.
- Avoid extreme temperatures and wear proper protection in cold weather.
Medical Treatment for Severe Cases:
- Doctors may recommend medications to improve circulation and reduce symptoms.
- If you experience persistent tightness, pain, or worsening colour changes, consult a doctor to rule out other conditions affecting blood flow.
2. Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) and Reduced Blood Flow
What is Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)?
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) reduces blood flow to the legs and feet. It is often caused by atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up in the arteries, restricting circulation.
Symptoms of PAD:
As blood circulation decreases, individuals may experience:
- Leg pain and weakness
- Cramping
- Swelling in the feet
- Numb toes
- Pale or blue feet
In advanced cases, tissue death or gangrene may occur, sometimes leading to the need for amputation.
Risk Factors for PAD:
The risk of developing PAD is higher for individuals who:
- Smoke
- Have high blood pressure
- Have diabetes
- Have high cholesterol
- Are over 60 years old
Managing and Treating PAD:
- Lifestyle changes such as exercise and a healthy diet can help manage the condition.
- In more severe cases, prescription medications or surgical procedures may be necessary to improve blood flow.
3. Frostbite and Cold-Related Tissue Damage
What is Frostbite?
Frostbite occurs when the skin and tissues are damaged by prolonged exposure to freezing temperatures. The toes, fingers, and feet are particularly vulnerable to it.
Symptoms of Frostbite:
When frostbite sets in, the affected areas may:
- Change colour: Turning purple, red, or black
- Feel numb or experience pins and needles
- Develop a hard or waxy appearance
In severe cases, permanent damage may occur, and amputation could be necessary.
Risk Factors for Frostbite:
Individuals at higher risk include those with:
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
- Raynaud’s Disease
- A history of previous frostbite
Preventing Frostbite:
- Dress warmly, especially in extreme cold.
- Wear warm socks and gloves.
- Avoid wet conditions that can increase heat loss.
- Monitor your skin for visual changes like gray or purple discoloration.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
If symptoms of frostbite appear, seek medical attention immediately to prevent further complications.
.
4. Varicose Veins and Blood Vessel Swelling
What are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins are swollen and twisted blood vessels commonly appearing on the legs and feet, often showing as dark purple or blue.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins:
Individuals with varicose veins may experience:
- Aching and burning sensations
- Muscle cramps, especially at night
- Swollen ankles and feet
- Heavy or uncomfortable legs
- In severe cases, skin ulcers or scrapes may develop.
Risk Factors for Varicose Veins:
People at higher risk include those who are:
- Female
- Older
- Overweight
- Genetically predisposed (family history of varicose veins)
- Standing for extended periods can worsen symptoms by affecting blood flow.
Treatment Options:
- Sclerotherapy: A treatment where foam is injected into the affected veins to reduce their appearance.
- Surgical removal: In more severe cases, surgery can remove damaged veins.
Managing Varicose Veins:
- Exercise regularly to promote circulation.
- Avoid prolonged standing to reduce pressure on veins.
- Apply heat therapy to help relieve discomfort.
Complications if Left Untreated:
If varicose veins are not treated:
- They may become more visible and worsen over time.
- The skin may thin out, leading to increased skin damage.
- Itching, pain, and slow-healing injuries can occur due to impaired circulation.
Those with chronic venous insufficiency should seek medical attention from a phlebologist.

Common Symptoms of Discolored Feet
What Causes Discolored Feet?
Discolored feet indicate various health issues, often related to poor blood circulation. It is crucial to identify the underlying cause to ensure proper treatment.
Symptoms of Circulation Problems:
- Swelling and pain in the feet
- Cold toes and fingers
- Skin discolouration: Blue, grey, or pale skin
- Itching or varicose veins
- Slow blood flow (Secondary Acrocyanosis), leading to pale or grey skin
- In severe cases, a popping sound may be heard during an injury.
Potential Complications:
- Skin ulcers can develop, mainly if chronic venous insufficiency is present.
- Persistent symptoms may signal a serious underlying condition requiring medical attention.
When to See a Healthcare Provider:
- If symptoms persist or worsen, a healthcare provider should evaluate your condition.
- Primary Acrocyanosis, though generally less severe, still requires monitoring to prevent complications.
- A personalized treatment plan can help address the cause of foot discolouration and improve circulation.
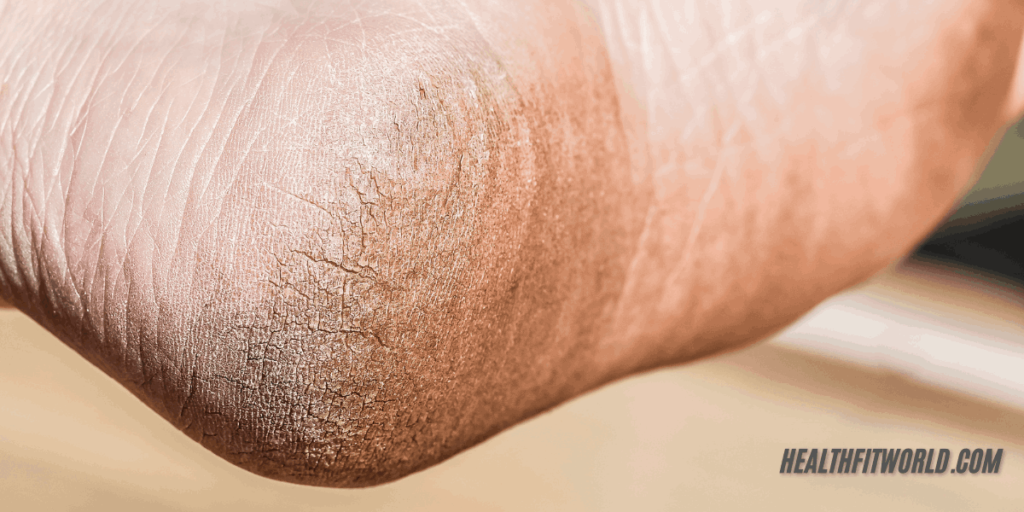
How to Prevent Heel Pain and Discoloration?
Reduce Stress on Your Feet
- Wear properly fitting shoes that provide adequate support.
- Use heel pads to absorb pressure and protect your soles, especially when standing on hard surfaces or walking for long periods.
- Maintain a moderate body weight to reduce pressure on your feet.
- Rest your feet whenever possible to avoid overuse and excessive strain.
Protect Your Feet from Cold-Related Discoloration
- Use warm blankets or thermal socks in colder weather to prevent primary acrocyanosis.
- Hand warmers and gloves can help regulate body temperature when exposed to cold conditions.
- For secondary acrocyanosis, manage underlying health conditions and avoid prolonged cold exposure.
Reducing foot strain, staying warm, and managing health conditions can help prevent heel pain and discolouration.
Treating Discoloration on Ankles and Feet
Addressing the Root Cause:
Identifying the underlying issue—poor circulation, swelling, or chronic skin conditions—is crucial for effectively treating discolouration on the ankles and feet.
Improving Blood Circulation:
- Elevate your legs to enhance blood flow and minimize swelling.
- Wear compression stockings to support healthy circulation and reduce venous insufficiency.
- Regular physical activity, such as walking or running, boosts circulation and prevents swelling.
- Avoid prolonged sitting or standing, as it can worsen symptoms.
Treating Irritation, Bruising, and Skin Conditions:
- Arnica gel can speed healing and reduce discolouration from bruises or red irritation.
- Consult a healthcare provider for antifungal medications or antibiotics for stasis dermatitis or skin infections.
- Keep the skin clean and hydrated to prevent further damage and support healing.
Medical Treatments for Severe Cases:
- Sclerotherapy can help treat venous issues and improve discolouration.
- Cold compress therapy may reduce inflammation and improve the skin’s appearance.
- Venous stasis ulcer management may be required for advanced cases to prevent further damage.
- A healthcare provider may recommend Laser treatment or vein-stripping surgery for severe venous insufficiency.
Pain and Inflammation Relief:
- NSAIDs can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Applying an ice pack can relieve swelling and discomfort.
- Physical therapy strengthens lower leg muscles to improve overall foot health.
- Using orthotics and insoles can correct foot deformities and relieve pressure.
Managing Secondary Acrocyanosis:
- Antiperspirants like Drysol or anticholinergics help control excessive sweating, particularly in cold conditions.
Preventing and Reducing Discoloration:
- Wearing supportive shoes can ease discomfort and prevent further damage.
- Maintaining a moderate body weight helps reduce pressure on the feet.
- Starting the day with hot water and lemon may aid circulation and overall health.
- Incorporating a yoga routine can help promote flexibility and blood flow.
Importance of Professional Consultation:
- A podiatrist consultation is necessary to diagnose if the discolouration is brown or associated with open wounds.
- An initial consultation with a healthcare provider ensures the right treatment plan is tailored to your needs.
You can effectively manage foot discolouration and improve overall foot health by addressing the root cause, following treatment recommendations, and making lifestyle adjustments.
Summary: Discolored Feet
Discoloured feet indicate various underlying health conditions, from circulation problems to vascular diseases and skin disorders. Recognizing the cause is crucial for effective treatment and long-term foot health. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve overall well-being, whether the discolouration is due to poor blood flow, chronic venous insufficiency, frostbite, or varicose veins. Simple lifestyle changes such as elevating the legs, wearing compression stockings, maintaining an active routine, and keeping feet warm in cold conditions can significantly improve circulation and reduce symptoms.
Seeking medical attention when symptoms persist or worsen is essential to rule out severe conditions and receive appropriate treatment. Various options exist, from medications to surgical interventions to restore proper blood flow and relieve discomfort. By understanding the causes of foot discolouration and implementing preventive measures, individuals can maintain healthy feet, reduce the risk of complications, and improve overall circulation and vascular health.